The Ryzen 7000 series is in the talks since it dethroned the Ryzen 5000 family as well as Intel’s Alder Lake series which have been one of the best processors for gaming and productivity for quite some time.
Being PC hardware lovers, many are looking for a good upgrade or building a completely new PC that can offer them the performance they want without overspending and that’s why it is important to focus on every component you buy.
Today we are looking at the Ryzen 9 7950X and the previous gen Ryzen 9 5950X to see which gives you a better value for the money. Although, the 7950X wins by default, there are still a lot of factors that will decide the winner between the two.
Specifications Difference
SPECS | AMD RYZEN 9 7950X | AMD RYZEN 9 5950X |
Code Name | Raphael | Vermeer |
Lithography | 5nm | 7nm |
Socket | AM5 | AM5 |
Cores/Threads | 16/32 | 16/32 |
Clock Speeds | 4.5/5.7GHz | 3.4/4.9GHz |
L2/L3 Cache | 16/64MB | 8/64MB |
TDP | 170W | 105W |
Integrated Graphics | Yes | No |
The specs difference is obvious. While many of the specs have been retained on the 7950X, it still brings some significant changes that theoretically increase its capability to outperform the 5950X in gaming and applications.
We can see that the biggest difference between the two is the core clocks. The clock speeds of 7950X are roughly 1GHz higher than those of 5950X and that contributes to 50% of the total performance boost.
Moreover, the power consumption of now increased to 170W from 105W. AMD made the AM5 socket more power-hungrier than the AM4 with 230W of Peak Power Consumption which is roughly 90W more than the PPT of AM4.
The L2 cache is also doubled which further enhances the IPC of 7950X as it is faster than the L3 cache even though the latter is still the same size as of 5950X.
Architectural Difference
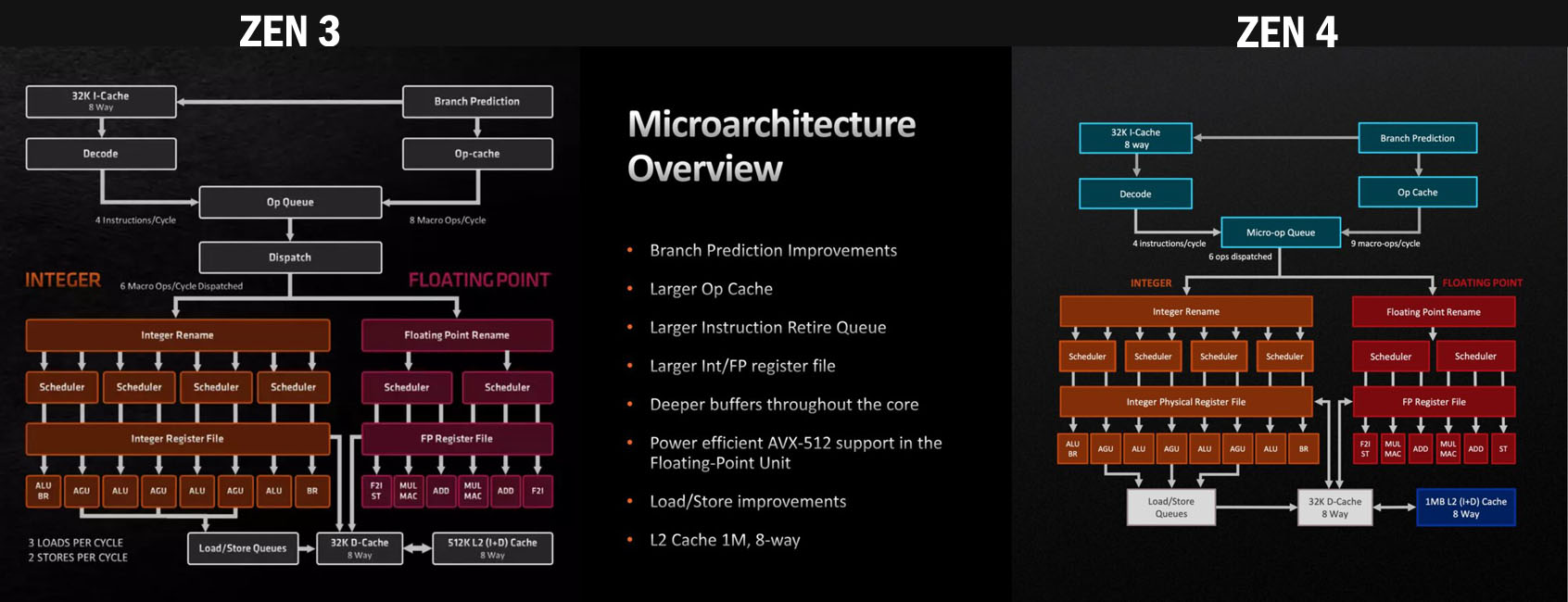
As you can see above, this is the essential block diagram comparison between Zen 3 and Zen 4. The 7950X uses the latest Zen 4 architecture that provides up to 13% more IPC than the Zen 3 due to having improvements in Front End, Execution Engine, and Load Store Advances.
The IPC lift is still not as big as between Zen 2 and Zen 3 though. Most of the gains are obtained through increasing the power consumption and the clock speeds as I said above. As Zen 4 is not made from scratch, huge changes couldn’t be made on the Zen 4 die.
As for the availability of L3 cache memory which made Zen 3 outstanding, Zen 4 is still able to access all the L3 cache memory of up to 32MB for 8 cores. That makes 64MB of L3 cache available to 16 cores on both the 7950X and 5950X each where each core gets 4MB of L3 cache.
However, the die design is a little different. Zen 4 is more similar to Zen 2 than Zen 3 in a way that now the Zen 4 die comes with two CCX per CCD. In simple words, the 7950X comes with two CCDs where each CCD comprises two CCXs having 4 cores each. This is similar to the Zen 2 block design.
Zen 3 on the other hand, doesn’t bring two CCXs per CCD but brings a single CCD for 8 cores that make two CCDs for 5950X where each CCD is comprised of 8 cores.
- Processor consumes less power to offer maximum...
- Ryzen 9 product line processor for better...
- 5 nm process technology provides optimal...
- Hexadeca-core (16 Core) processor core efficiently...
Motherboard Compatibility

Since the first Ryzen generation, the motherboard socket didn’t change. From the first Ryzen 1000 series to the 5000 series, every processor is compatible with the AM4 socket. This changes with the release of the Ryzen 7000 series.
Ryzen 7950X is now only compatible with the AM5 socket which features a totally different type of grid. Typically, AMD uses PGA(Pin Grid Array) type sockets for its motherboards that include the FM2, AM3, and AM4 for the 5950X.
The AM5 socket is now LGA(Land Grid Array) which is what Intel has been using for decades. This gives the motherboard socket the pin grid instead of the processors. This is a big change AMD has made after a long time.
As AM5 is completely new, there are very few chipsets that can be found on AM5 motherboards. There are only four- X670, X670E, B650, and B650E where the “E” stands for Extreme that provides more PCI-E 5.0 lanes.
AM4, on the other hand, has a total of 9 chipsets including all the locked and unlocked chipsets. These include all the 300, 400, and 500 chipsets. So, the 5950X has comparatively much higher compatibility with a wide range of motherboards.
RAM Compatibility
Ryzen 7950X and 5900X use different motherboards and therefore, different RAM too. AM4 platform only supports DDR4 memories and AM5 only DDR5.
DDR4 RAM can’t be used on AM5 motherboards and the same goes for AM4 and DDR5 RAM. DDR5 RAM is significantly faster at clock speeds than DDR4 but also brings higher latency timings. Apparently, they both look identical in terms of pin layout but the cutout is a little shifted toward the other side on DDR4.
Integrated Graphics

One more big difference between the two is the iGPU. Ryzen CPUs are known for not having any integrated graphics. Only the APUs feature iGPUs and we have a separate list of those.
The Ryzen 7000 changes this norm and brings iGPU on the chipset itself. The 7950X comes with RDNA 2 based iGPU with 2 cores clocked at 400-2000MHz. The 5950X doesn’t have any iGPU on the chip.
This can be a game changer for many as the 7950X won’t need any discrete GPU solution for powering the display. However, the iGPU used in it is not powerful enough to play games but can surely do the basic stuff.
Gaming And Application Performance
Here comes the most interesting part. While we have already discussed the difference between the two CPUs in specs, architecture, and compatibility, the benchmarks will tell us the whole story.
It won’t be a fair comparison if we don’t consider their real-world benchmarks in gaming and particularly in CPU-dependent applications as the 7950X and 5950X are specially made for the latter. For this purpose, we are going to compare and analyze a few benchmarks from some reliable third-party sources to see how much of an average difference you should be expecting.
We are considering benchmarks from GamersNexus((https://youtu.be/s04TOQkzv3c)), Tomshardware((https://www.tomshardware.com/reviews/amd-ryzen-9-7950x-ryzen-5-7600x-cpu-review)), Guru3D((https://www.guru3d.com/articles_pages/amd_ryzen_9_7900x_processor_review,1.html)), and Techspot((https://www.techspot.com/review/2538-amd-ryzen-7900x/)) for this purpose. Remember that each of the sources uses different configurations, different games, and applications, and have tested them in different environments with some overlapping in each area. However, this will give us a rough idea of how good the 7950X is over the 5950X.
As far as the gaming benchmarks go, the performance gap between the two looks the same across all tests with the 7950X beating the 5950X by 16-20% . There isn’t much to talk about this as we already know that most PC users are going to buy either of these two CPUs for professional applications.
In CPU-dependent and professional applications, no benchmark between any of the considered sources showed similar results except that in every test the 7950X was significantly faster than the 5950X . The results differed by a huge margin across these sources. So, here is the rough idea.
The 7950X is above 20% faster in single-thread and up to 50% in multi-thread performance in Cinebench R23. The scores varied hugely in the multi-threaded Cinebench test but you can expect the margin to be around 40-50% at the minimum. The 7950X is also significantly faster in compression and decompression with somewhere around 30% higher scores even though the 5950X is still the second-fastest decompressing CPU.
Blender shows a similar result but more performance gap that exceeds 50% in some cases. The 7950X is also around 15-25% faster in video encoding and gives around 20-30% faster rendering in Adobe Premiere Pro. The story is the same with Adobe Photoshop with a difference of around 24 percent giving the 7950X a huge lead.
Thermals And Power Consumption
The 7000 series runs hot whether you consider the 7950X or any other Ryzen 7000 CPU. It runs much hotter than any other previous Ryzen CPUs.
The 7950X runs particularly hotter than all the 7000 CPUs due to having more cores. The temperature hovers around 95C as per various tests which is also the max operating temperature of the 7950X but AMD still calls it normal.
Ryzen 5950X doesn’t have this problem and can be cooled with any decent 280 or 360mm AIO. The 7950X doesn’t seem to benefit at all no matter how good the CPU cooler you use. This is why we only recommend going with the premium AIO cooling solutions for the 7950X.
Power consumption is another factor here that some users may consider. The 7950X is rated at 170W but can easily surpass 200W even without overclocking. As the AM5 socket is rated at 230W, the total power consumption of the 7950X alone sometimes crosses this line which I believe is really concerning.
The 5950X is rated at a much lower TDP of 105W and stays at a healthy 120W which is below the maximum power rating of the AM4 socket.
Which Is Better?
There is no debate on whether the 7950X is faster than the 5950X. It is comparatively faster in both gaming and non-gaming applications but comes at some disadvantages, pricing is not one of those in my opinion.
The biggest concern is the power consumption and thermals which exceed the normal ratings. Also, the cost of high-end AM5 motherboards will be at least $500+ whereas the high-end AM4 motherboards can be bought for around $300.
DDR5 memories are also very expensive and so is the cost of premium 360mm AIO coolers. So, this makes the total cost of the build with the 7950X much higher than using 5950X.
On the other hand, 7950X is really the best Ryzen CPU you can have right now and gives you the freedom to upgrade much more easily. With the AM4 platform, you cannot go higher than 5950X which is already a top of the line Ryzen 5000 CPU.
You will need to change your motherboard, RAM, and possibly a CPU cooler altogether if you are looking for an upgrade to an AM5-based PC.
Over To You
I have explained the key differences between 7950X and 5950X in detail and the choice is yours. If you think upgradeability matters more, then go with the 7950X but if you think thermals, power consumption, and lower cost of the build is what you need, then consider the 5950X.

Reasons To Buy Ryzen 9 7950X
[wp-svg-icons icon=”thumbs-up” wrap=”i” color=green] AM5 will last longer
[wp-svg-icons icon=”thumbs-up” wrap=”i” color=green] RDNA 2 based iGPU

Reasons To Buy Ryzen 9 5950X
[wp-svg-icons icon=”thumbs-up” wrap=”i” color=green] Better thermals and lower power consumption
[wp-svg-icons icon=”thumbs-up” wrap=”i” color=green] Supports less expensive DDR4 RAM
Related:
- AMD Ryzen 5 7600X vs Ryzen 7 7700X
- AMD Ryzen 5 7600X vs Ryzen 5 5600X
- AMD Ryzen 5 7600X vs Intel Core i5 12600K
- AMD Ryzen 5 7600X vs Ryzen 7 5800X3D
- AMD Ryzen 7 7700X vs Ryzen 7 5800X3D
- AMD Ryzen 7 7700X vs Intel Core i7 12700K
- AMD Ryzen 7 7700X vs Ryzen 9 7900X
- AMD Ryzen 9 7900X vs Ryzen 9 7950X
- AMD Ryzen 9 7900X vs Intel Core i9 12900K
- AMD Ryzen 5 7600X vs Intel Core i9 12900K
- AMD Ryzen 7 7700X vs Ryzen 7 5700X
- AMD Ryzen 9 7900X vs Ryzen 9 5900X



