Among the best benefits of building a desktop computer is that you can easily upgrade whatever component you want but this is not true in the case of a laptop.
While certainly, laptops allow upgrading of several other components like RAM and storage drive, when it comes to changing other parts such as motherboard or CPU, they depend on several conditions.
Let’s take a look at what you need to know if you want to change your laptop processor.
Why It Is Harder To Change Processor On A Laptop?
On desktop computers, you will see individual parts installed on the motherboard and the case. Each part can be removed or installed easily as there is a lot of room for installation and upgrades.
On desktop motherboards, you will see two types of sockets- LGA(Land Grid Array) and PGA(Pin Grid Array). In both the sockets, you can simply drop your CPU and secure it by putting the lever back. It’s that easy but on a laptop, we don’t see these types of sockets often.
Instead, laptops generally use the BGA socket A.K.A Ball Grid Socket that doesn’t allow processors to be removed easily. Instead, the processor is soldered to the socket and therefore, becomes undetachable.
The reason for using a BGA socket is the compactness of a laptop. Laptop manufacturers have to fit all the components horizontally on the motherboard to save as much space as possible. Therefore, the processor, GPU, and even the RAM are installed in an overlapping fashion.
Related- What RAM is compatible with my laptop?
Only laptops with either LGA or PGA sockets can allow you to upgrade your processor but generally, these laptops are limited and still require a lot of attention to other details before upgrading the processor.
How To Check Compatibility?
To upgrade a laptop processor you need to check a few things before proceeding. These are the socket, generation, and TDP.
If you are looking to upgrade the processor, the first condition will always be the socket type. If the laptop is having a BGA socket, there is no way to change your CPU. Any other socket will allow you to upgrade but you must be thinking about how you can know what socket your laptop has.
Generally, the way to know the motherboard socket of your laptop is not by checking the laptop specs but instead by the specs of your laptop processor.
Identifying The Processor And The Socket
AMD and Intel have a complete list of their desktop and laptop processors on their websites and they generally end up with letters like “H”, “U”, “P” etc. You can easily know your laptop processor model by checking the specs of your laptop which can be known from the laptop itself.
You can use Windows 10 methods for knowing the specs of your laptop or you can also check on the laptop manufacturer’s website.
Now enter the CPU model name on your browser and open the specs page of your processor. Both AMD and Intel have detailed specs on their websites where you can scroll down and find out the socket your processor is compatible with.
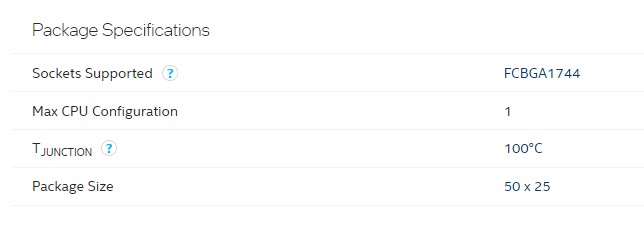
Intel laptop CPUs socket will be found in the above format while AMD uses FP5, FP6, and FP7 as socket names for Ryzen laptop CPUs. They are also BGA and therefore, if you see the FP format on a Ryzen laptop CPU, it means they are BGA and can’t be upgraded.
The laptops with upgradeable processors generally use the same socket present on the desktop motherboards. So, suppose your laptop features an LGA 1700 socket, you can easily change your CPU by putting another Intel 12th gen CPU. The same goes for AMD laptops with sockets like AM4.
Generation
Once, you identify the socket, it’s also important to find the correct generation. While most Intel laptops use a different socket for one or two generations, AMD uses the same socket for more than one generation.
So suppose, if the laptop you are using has an LGA 1700 socket, you cannot put a 10th or 11th gen Intel CPU but only a CPU belonging to the same generation i.e., 12th gen or 13th gen as both use the same sockets.
With that, you also have to keep in mind that you must update your BIOS if you are changing your generation as the default BIOS may not support the next generation without the proper BIOS version.
What RAM Is Compatible With My Laptop? Easy Method To Know
TDP
Lastly, it is also important to check the TDP rating of your laptop. Going from a low-end to a high-end CPU in a laptop requires careful inspection as the laptop’s battery may not be sufficient for a long backup as it was originally designed for a low-end CPU.
While most users will try to change their processors differing in specs and performance significantly, upgrading to a CPU that is similar in specs like core count, cache, and TDP will have no problem.
Upgrading to a higher-end CPU also means more heat generation and your laptop may not be ready for that as it was originally designed to dissipate the heat of an inferior processor. Keep all that in mind if you don’t want your laptop to die sooner.
Upgrading Laptop Processor From i3 To i7 And Such
Upgrading Intel CPUs from i3 to i5, i3 to i7, and i5 to i7 is not a big issue if your laptop is featuring an LGA socket. The socket must be the same and it should be compatible with the generation you are going for the upgrade.
Let’s assume that you are using a laptop that boasts an LGA 1151 socket and a Core i3 9th gen CPU. If you try to put a Core i5 processor that is compatible with the LGA 1200 socket and belongs to the 10th gen, you won’t be able to. You can only upgrade to a Core i5 or Core i7 9th gen CPU on an LGA 1151 socket that supports the 9th gen family.
The same goes for other Intel and AMD sockets.
How Likely Your Laptop Processor Is Upgradeable?
Very unlikely, I am are afraid. There are only a handful of laptops that allow upgrading of processors. Most laptop manufacturers like MSI, Asus, HP, and Dell generally don’t manufacture laptops with LGA and PGA sockets.
As opening laptops and changing their components may lead to physical damage easily, laptop manufacturers generally don’t allow processor upgrading. However, some unpopular manufacturers are producing a handful of laptops that allow processor upgrades.
A Chinese laptop manufacturer Hasee launched Hasee ZX9 gaming laptops with three variations that feature the LGA 1700 socket for Intel 12th gen processors. These are significantly more expensive than non-upgradeable laptops with the same configuration.
Final Words
We don’t encourage going with upgradeable laptops nor do we recommend upgrading the BGA socket laptop processors. They can be costly and the process of upgrading can void your warranty. You should always buy a laptop keeping in mind that you won’t be able to upgrade your processor.